Introduction
If you’ve been exploring web hosting options, you’ve likely come across the term VPS, or Virtual Private Server. It’s a popular choice for many businesses and developers who need more than what basic shared hosting offers but aren’t ready for the commitment of a dedicated server. But what exactly is a VPS server, and how can it be used? Let’s break it down.
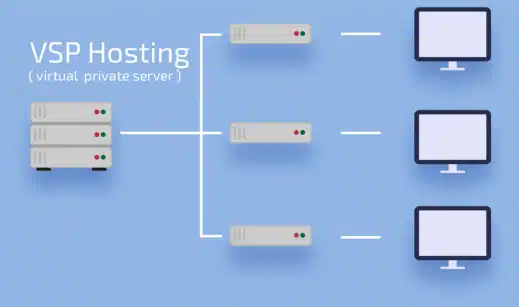
Understanding VPS Hosting
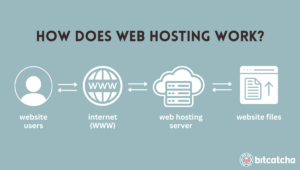
How VPS Hosting Works
A VPS server is a virtualized environment created within a physical server. This virtualization technology allows a single physical server to be divided into multiple virtual compartments, each acting as an independent server. Each VPS operates with its own operating system (OS), resources, and configurations, giving users a level of control similar to that of a dedicated server but at a lower cost.
Differences Between VPS and Other Hosting Types
- Shared Hosting: In shared hosting, multiple websites share the same server and resources. This is the most basic and affordable type of hosting but offers limited control and performance.
- Dedicated Hosting: A dedicated server provides the entire physical server to a single user, offering maximum resources and control, but it’s more expensive.
- Cloud Hosting: This type of hosting uses a network of servers to provide resources, offering scalability and redundancy. It’s similar to VPS but operates across multiple physical servers.
Key Features of VPS Hosting
VPS hosting is characterized by its balance of performance, control, and cost. Key features include dedicated resources (CPU, RAM, storage), full root access, and the ability to install custom software and configurations.
Common Uses of VPS Servers
Hosting Websites
One of the primary uses of a VPS server is hosting websites. Whether it’s a personal blog, a business site, or a complex web application, a VPS provides the resources and flexibility needed to handle traffic and customize the server environment to meet specific needs.
Running Applications and Software
VPS servers are ideal for running custom applications or software that require specific configurations or resources. Developers often use VPS to host applications that need to run 24/7, such as APIs, backend services, or even small-scale SaaS platforms.
Hosting Online Stores (E-commerce)
E-commerce websites, with their need for security, reliability, and performance, often benefit from VPS hosting. A VPS server can handle payment processing, secure customer data, and ensure that the online store runs smoothly even during high-traffic periods.
Creating a Development Environment
Developers often use VPS servers to create isolated environments where they can build, test, and deploy applications without affecting live environments. This is especially useful for testing new features, updates, or code before pushing them to production.
Managing Databases
A VPS can be used to host databases for applications or websites. With the dedicated resources of a VPS, database performance can be optimized, ensuring fast data retrieval and handling.
Hosting Game Servers
VPS servers are popular for hosting game servers, where players can connect and play multiplayer games. The control and resources provided by a VPS allow for customization and smooth gameplay, even with multiple players online.
Advantages of Using a VPS Server
Improved Performance and Speed
Since a VPS provides dedicated resources, there’s no competition with other users for CPU, RAM, or bandwidth. This results in better performance and faster load times compared to shared hosting.
Greater Control and Customization
With full root access, you have complete control over your VPS environment. You can install custom software, configure settings, and tweak performance to meet your specific needs.
Enhanced Security
A VPS offers a higher level of security than shared hosting, as your environment is isolated from other users. This reduces the risk of security breaches and allows you to implement custom security measures.
Scalability for Growing Websites
As your website or application grows, you can easily scale your VPS by upgrading your resources. This flexibility is crucial for businesses expecting traffic spikes or gradual growth.
Cost-Effectiveness Compared to Dedicated Hosting
While a VPS offers many of the benefits of a dedicated server, it comes at a fraction of the cost. This makes it an attractive option for businesses that need more than shared hosting but aren’t ready for the financial commitment of a dedicated server.
Who Should Use a VPS Server?
Small to Medium-Sized Businesses
SMBs that have outgrown shared hosting but don’t need a dedicated server often find VPS hosting to be the perfect middle ground. It offers the necessary resources and control to manage business operations effectively.
Developers and Programmers
For developers who need a flexible environment to build and test applications, a VPS is ideal. It allows for the installation of development tools and provides the stability needed for continuous integration and deployment.
E-commerce Websites
E-commerce sites that require reliable performance, secure transactions, and the ability to handle high traffic will benefit from the dedicated resources of a VPS server.
Bloggers with High Traffic
For bloggers whose sites are attracting significant traffic, a VPS can provide the performance needed to keep the site running smoothly, even during peak periods.
Startups Looking for Growth Potential
Startups that anticipate rapid growth can start with a VPS and scale up as needed. This ensures they have the resources to support their expanding business without overcommitting early on.
How to Choose the Right VPS Plan
Assessing Your Needs
Before selecting a VPS plan, consider your website or application’s specific needs in terms of traffic, storage, and budget. Understanding these requirements will help you choose the right level of resources.
Choosing the Right Operating System
VPS servers can run on Linux or Windows, depending on your preference and the software you plan to use. Linux is popular for its stability and open-source nature, while Windows may be necessary for specific applications.
Understanding Resource Allocation
Look at the CPU, RAM, and storage options available in VPS plans. Ensure the plan you choose can handle your expected traffic and workload without bottlenecks.
Evaluating Hosting Providers and Support Options
Not all VPS providers are created equal. Research hosting companies to find those with a strong reputation for reliability, security, and customer support. Managed VPS options are available for those who prefer not to handle server maintenance themselves.
VPS Server Management
Unmanaged vs. Managed VPS Hosting
Unmanaged VPS hosting gives you full control over the server, but you’re responsible for all maintenance, security, and updates. Managed VPS hosting, on the other hand, includes these services, allowing you to focus on your website or application.
Common Management Tasks
Managing a VPS involves tasks like regular software updates, security patches, performance monitoring, and backups. These tasks are crucial to keeping your server running smoothly and securely.
Using Control Panels for Easy Management
Control panels like cPanel or Plesk can simplify VPS management by providing a user-friendly interface for tasks like setting up email accounts, managing databases, and configuring security settings.
Security Best Practices for VPS Servers
Setting Up Firewalls and Security Configurations
Ensure your VPS is protected by a robust firewall and configure security settings to minimize vulnerabilities. Regularly update your software to protect against the latest threats.
Regular Backups and Data Protection
Set up automated backups to protect your data in case of server failure or other issues. Having backups ensures you can quickly restore your server to a previous state if needed.
Monitoring for Security Threats
Implement monitoring tools to keep an eye on your server’s activity. This helps in identifying and responding to potential security threats before they can cause damage.
When to Upgrade from VPS to Dedicated Hosting
Signs You’ve Outgrown Your VPS
If your website or application is consistently maxing out the resources of your VPS, it might be time to consider upgrading to a dedicated server. Other signs include frequent downtime, slow performance, and the need for more advanced security features.
Benefits of Moving to a Dedicated Server
Upgrading to a dedicated server gives you access to all the resources of a physical server, providing unparalleled performance, control, and security. This is ideal for large businesses or high-traffic websites that require top-tier hosting.
Conclusion
A VPS server offers a versatile, scalable, and cost-effective solution for hosting websites, running applications, managing databases, and more. It strikes a balance between shared and dedicated hosting, making it a popular choice for small to medium-sized businesses, developers, and anyone looking for more control over their hosting environment. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to grow, a VPS can provide the resources and flexibility you need to succeed.
FAQs
- What is the difference between VPS and shared hosting?
- VPS hosting offers dedicated resources and more control compared to shared hosting, where resources are shared among multiple users.
- Can I upgrade from a VPS to a dedicated server?
- Yes, most hosting providers offer the option to upgrade from a VPS to a dedicated server as your needs grow.
- Is VPS hosting suitable for beginners?
- VPS hosting can be suitable for beginners if they choose a managed VPS plan, where the provider handles most of the technical tasks.
- How secure is a VPS server?
- A VPS server is generally more secure than shared hosting because of its isolated environment. Security can be further enhanced with proper configurations and practices.
- What are the typical costs of a VPS server?
- VPS server costs vary depending on the resources and features offered, but they generally range from $10 to $100+ per month, depending on the provider and plan.